

From Knowledge to Yield — Empowering Cassava Seed Systems.
Building Capacity is a practical, strategy-driven toolkit designed to strengthen cassava seed systems by addressing the core capacity gaps faced by seed producers. It offers tailored training resources, business development tools, and partnership frameworks to improve technical skills, market access, and regulatory collaboration. By equipping actors with the right knowledge and support, Building Capacity enhances seed quality, boosts productivity, and promotes a sustainable, profitable future for cassava and other vegetatively propagated crops.
This technology is pre-validated.
Adults 18 and over: Positive high
The poor: Positive high
Under 18: Positive medium
Women: Positive high
Climate adaptability: Highly adaptable
Farmer climate change readiness: Significant improvement
Biodiversity: Positive impact on biodiversity
Carbon footprint: Much less carbon released
Environmental health: Does not improve environmental health
Soil quality: Does not affect soil health and fertility
Water use: Same amount of water used
The Building Capacity toolkit is a transformative solution designed to strengthen agricultural systems, focusing on enhancing seed production and addressing critical capacity gaps within the seed sector. It is an essential tool for development institutions aiming to contribute to sustainable agriculture, economic growth, gender equality, and climate resilience while fostering inclusive development.
By adopting the Building Capacity toolkit, development institutions can significantly improve seed quality, enhance productivity, and build strategic partnerships with key stakeholders such as seed regulatory agencies, research institutions, and agricultural extension services. This toolkit offers a comprehensive approach to supporting seed producers, ensuring that they have the tools, knowledge, and resources to thrive in the agricultural sector.
Key Activities for Adoption:
By adopting the Building Capacity toolkit, development institutions can transform agricultural seed systems, creating a sustainable and profitable future for seed producers. This technology supports broader economic development goals, promotes gender inclusivity, and helps to mitigate the impacts of climate change on agriculture, making it an indispensable tool for development success.
Capacity building for 1,350 farmers
Training manual development
Training Venue and other facilities
Facilitators Expense
Cost of printing the training materials
Unknown
Scaling Readiness describes how complete a technology’s development is and its ability to be scaled. It produces a score that measures a technology’s readiness along two axes: the level of maturity of the idea itself, and the level to which the technology has been used so far.
Each axis goes from 0 to 9 where 9 is the “ready-to-scale” status. For each technology profile in the e-catalogs we have documented the scaling readiness status from evidence given by the technology providers. The e-catalogs only showcase technologies for which the scaling readiness score is at least 8 for maturity of the idea and 7 for the level of use.
The graph below represents visually the scaling readiness status for this technology, you can see the label of each level by hovering your mouse cursor on the number.
Read more about scaling readiness ›
Uncontrolled environment: validated
Used by some intended users, in the real world
| Maturity of the idea | Level of use | |||||||||
| 9 | ||||||||||
| 8 | ||||||||||
| 7 | ||||||||||
| 6 | ||||||||||
| 5 | ||||||||||
| 4 | ||||||||||
| 3 | ||||||||||
| 2 | ||||||||||
| 1 | ||||||||||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | ||
| Country | Testing ongoing | Tested | Adopted |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ghana | –No ongoing testing | –Not tested | Adopted |
| Nigeria | –No ongoing testing | –Not tested | Adopted |
This technology can be used in the colored agro-ecological zones. Any zones shown in white are not suitable for this technology.
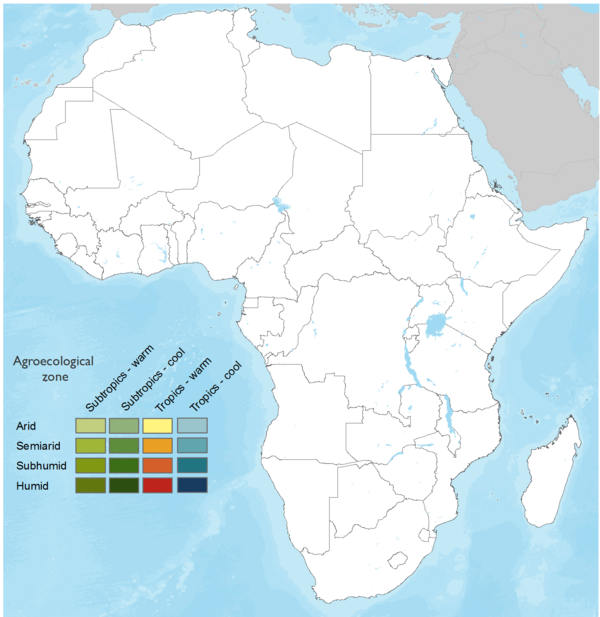













| AEZ | Subtropic - warm | Subtropic - cool | Tropic - warm | Tropic - cool |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Arid | ||||
| Semiarid | ||||
| Subhumid | ||||
| Humid |
Source: HarvestChoice/IFPRI 2009
The United Nations Sustainable Development Goals that are applicable to this technology.




Last updated on 30 June 2025