

Optimizing Pesticide Application for Sustainable Agriculture
The Crop Sprayer App enables users to determine accurate pesticide dosages by considering factors such as sprayer tank size, sprayer output, and application area. It calculates the amount of pesticide concentrate needed per tank and the total quantity for the entire spraying operation. The app operates offline after initial download, ensuring accessibility in remote areas.
This technology is pre-validated.
Adults 18 and over: Positive medium
Adult users will gain ability to quickly run important calculations on product use. This is to avoid errors during manual miscalculation which may increase risks to the individual and the environment, and cause more product to be applied than required.
The poor: Positive medium
Smallholder farmers in low and lower middle income countries are the ultimate beneficiary of this technology. Knowing the right application of crop protection products should reduce the risk of too much being purchased and applied.
Women: Positive medium
The tool has been designed to be available in local languages, and to work offline and on lower specification phones that we found women farmers and advisors have available.
Biodiversity: Not verified
The judicious use of crop protection products as a result of using the Crop Sprayer app may reduce run-off or impacts on non-target organisms, but this has not been tested.
Environmental health: Not verified
The judicious use of crop protection products as a result of using the Crop Sprayer app may reduce the amount of product that gets applied, and reduce the amount that may end up as run-off, but this has not been tested.
The Crop Sprayer App is designed to enhance agricultural productivity, promote environmental sustainability, and ensure the safety of pesticide applicators. By facilitating precise pesticide application, it contributes to efficient pest and disease management while mitigating the impacts of climate change.
To integrate this technology in your program, key activities are:
Open source / open access
Scaling Readiness describes how complete a technology’s development is and its ability to be scaled. It produces a score that measures a technology’s readiness along two axes: the level of maturity of the idea itself, and the level to which the technology has been used so far.
Each axis goes from 0 to 9 where 9 is the “ready-to-scale” status. For each technology profile in the e-catalogs we have documented the scaling readiness status from evidence given by the technology providers. The e-catalogs only showcase technologies for which the scaling readiness score is at least 8 for maturity of the idea and 7 for the level of use.
The graph below represents visually the scaling readiness status for this technology, you can see the label of each level by hovering your mouse cursor on the number.
Read more about scaling readiness ›
Uncontrolled environment: validated
Common use by projects NOT connected to technology provider
| Maturity of the idea | Level of use | |||||||||
| 9 | ||||||||||
| 8 | ||||||||||
| 7 | ||||||||||
| 6 | ||||||||||
| 5 | ||||||||||
| 4 | ||||||||||
| 3 | ||||||||||
| 2 | ||||||||||
| 1 | ||||||||||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | ||
| Country | Testing ongoing | Tested | Adopted |
|---|---|---|---|
| Burundi | –No ongoing testing | –Not tested | Adopted |
| Ethiopia | –No ongoing testing | –Not tested | Adopted |
| Ghana | –No ongoing testing | –Not tested | Adopted |
| Kenya | –No ongoing testing | –Not tested | Adopted |
| Malawi | –No ongoing testing | –Not tested | Adopted |
| Rwanda | –No ongoing testing | –Not tested | Adopted |
| South Sudan | –No ongoing testing | –Not tested | Adopted |
| Uganda | –No ongoing testing | –Not tested | Adopted |
| Zambia | –No ongoing testing | –Not tested | Adopted |
This technology can be used in the colored agro-ecological zones. Any zones shown in white are not suitable for this technology.
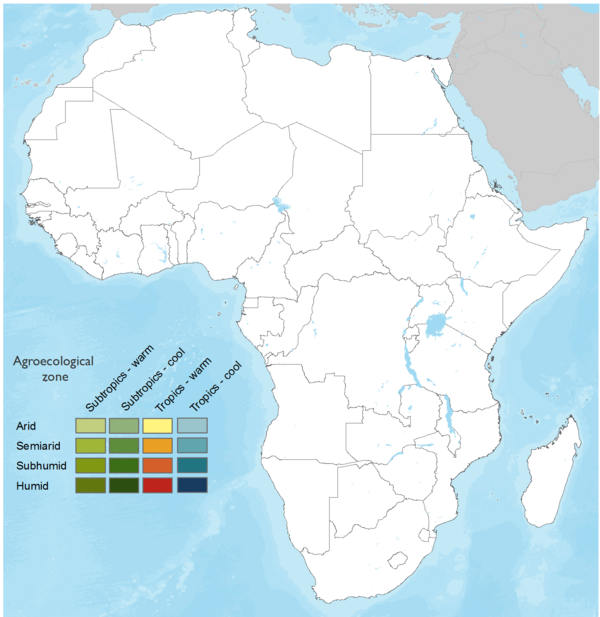








| AEZ | Subtropic - warm | Subtropic - cool | Tropic - warm | Tropic - cool |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Arid | – | – | – | – |
| Semiarid | – | – | ||
| Subhumid | ||||
| Humid |
Source: HarvestChoice/IFPRI 2009
The United Nations Sustainable Development Goals that are applicable to this technology.

Improves crop yields through effective pest management.

Enhances agricultural productivity and economic opportunities.

Encourages efficient use of agricultural inputs, reducing waste.
Last updated on 9 January 2026