

Boosting Aquaculture with Resilient, Fast-Growing Catfish Hybrids
Fast Growing and Hybrid African Catfish" is developed to enhance freshwater farming in Sub-Saharan Africa. This technology involves the selective breeding and hybridization of two catfish species to create a superior hybrid offspring (Hetero-Clarias). The process of hybridization requires hormone-induced egg release in female catfish and the collection of seminal fluids from male catfish, subsequently combined to produce the hybrid.
This technology is TAAT1 validated.
Adults 18 and over: Positive high
The poor: Positive medium
Under 18: No impact
Women: Positive high
Climate adaptability: Highly adaptable
Farmer climate change readiness: Significant improvement
Biodiversity: No impact on biodiversity
Carbon footprint: Same amount of carbon released
Environmental health: Moderately improves environmental health
Soil quality: Does not affect soil health and fertility
Water use: Same amount of water used
In the near future, this section will provide an overview of this technology's success in various contexts, details on partners offering technical support, training, and implementation monitoring, along with other valuable insights for your projects and programs. These details will be added progressively.
In the meantime, use the 'Request information' button if you need to contact us.
Feed inputs for 8600—10000 Catfish fingerlings
Open source / open access
Scaling Readiness describes how complete a technology’s development is and its ability to be scaled. It produces a score that measures a technology’s readiness along two axes: the level of maturity of the idea itself, and the level to which the technology has been used so far.
Each axis goes from 0 to 9 where 9 is the “ready-to-scale” status. For each technology profile in the e-catalogs we have documented the scaling readiness status from evidence given by the technology providers. The e-catalogs only showcase technologies for which the scaling readiness score is at least 8 for maturity of the idea and 7 for the level of use.
The graph below represents visually the scaling readiness status for this technology, you can see the label of each level by hovering your mouse cursor on the number.
Read more about scaling readiness ›
Semi-controlled environment: prototype
Common use by projects NOT connected to technology provider
| Maturity of the idea | Level of use | |||||||||
| 9 | ||||||||||
| 8 | ||||||||||
| 7 | ||||||||||
| 6 | ||||||||||
| 5 | ||||||||||
| 4 | ||||||||||
| 3 | ||||||||||
| 2 | ||||||||||
| 1 | ||||||||||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | ||
| Country | Testing ongoing | Tested | Adopted |
|---|---|---|---|
| Benin | –No ongoing testing | Tested | Adopted |
| Cameroon | –No ongoing testing | Tested | Adopted |
| Côte d’Ivoire | –No ongoing testing | Tested | Adopted |
| Democratic Republic of the Congo | –No ongoing testing | Tested | Adopted |
| Kenya | –No ongoing testing | Tested | Adopted |
| Malawi | –No ongoing testing | Tested | Adopted |
| Nigeria | –No ongoing testing | Tested | Adopted |
| Tanzania | –No ongoing testing | Tested | Adopted |
| Uganda | –No ongoing testing | Tested | Adopted |
| Zambia | –No ongoing testing | Tested | Adopted |
This technology can be used in the colored agro-ecological zones. Any zones shown in white are not suitable for this technology.
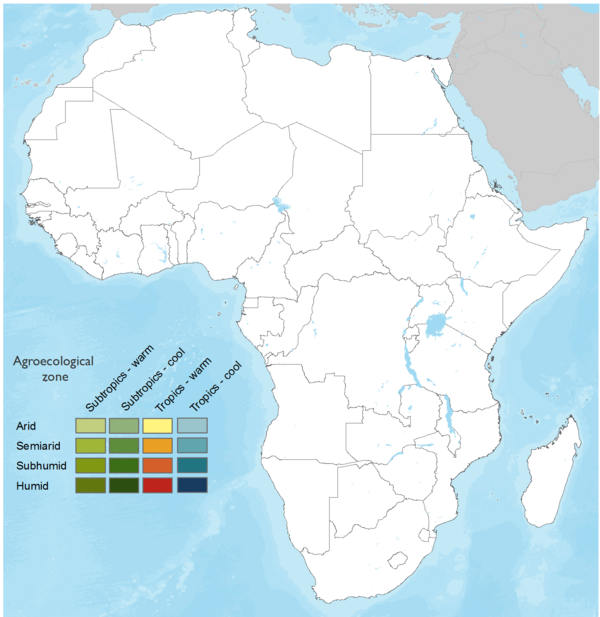




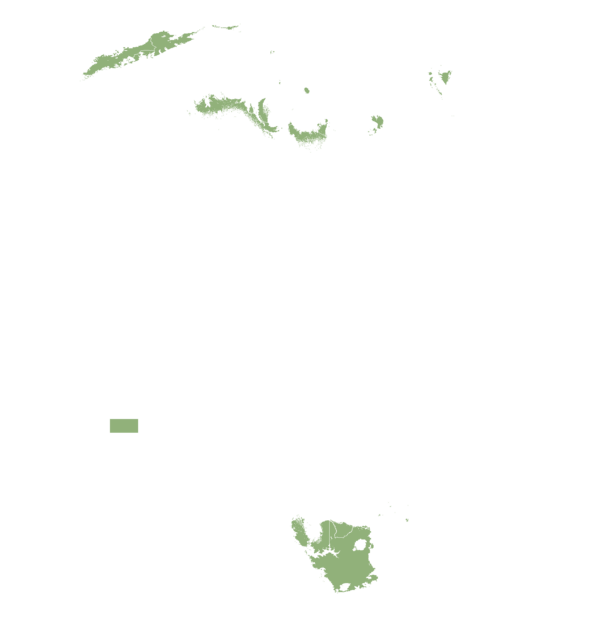
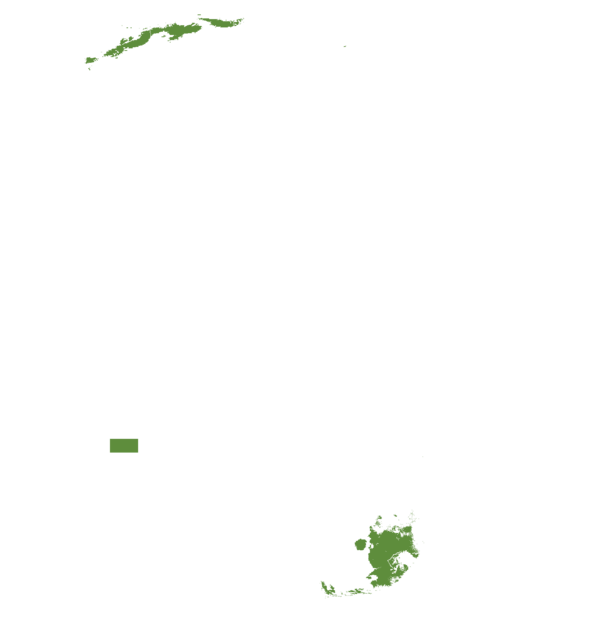







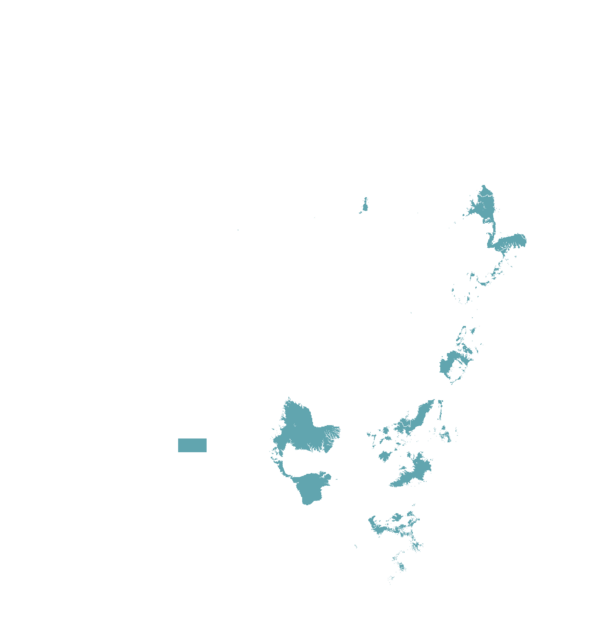


| AEZ | Subtropic - warm | Subtropic - cool | Tropic - warm | Tropic - cool |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Arid | ||||
| Semiarid | ||||
| Subhumid | ||||
| Humid |
Source: HarvestChoice/IFPRI 2009
The United Nations Sustainable Development Goals that are applicable to this technology.




Last updated on 31 October 2025