

From Advocacy to Action: Replicating Success with Lasting Investment
This technology is a model that helps governments and development partners improve cassava seed systems at national level. It uses advocacy, planning, and teamwork to create the right conditions for improved cassava seeds to be used widely and sustainably. The model does not produce seeds itself. Instead, it helps countries include good seed practices—like Early Generation Seed (EGS), SAH, nodal cuttings, and digital tools—into their public programs and policies. It supports local leadership, funding, and better coordination among all actors.
This technology is pre-validated.
Adults 18 and over: Positive high
Gain access to training, market opportunities, and investments through policy-driven support.
The poor: Positive medium
Supported through stronger, market-based seed systems that reduce dependence on free seed distribution.
Under 18: Positive medium
May benefit from inclusive frameworks, though not directly targeted by advocacy activities.
Women: Positive medium
Included indirectly through seed entrepreneurship and policy engagement, though not the primary focus.
Climate adaptability: Highly adaptable
The model works across diverse agro-ecological zones and promotes climate-resilient cassava seed technologies.
Farmer climate change readiness: Moderate improvement
Improves farmer preparedness by supporting access to climate-smart varieties and good practices through national programs.
Biodiversity: Positive impact on biodiversity
Encourages the use of multiple improved cassava varieties, helping reduce genetic erosion and supporting varietal diversity.
Carbon footprint: A bit less carbon released
Digital coordination and policy planning reduce the need for repeated physical meetings and seed distribution trips.
Environmental health: Moderately improves environmental health
Promotes clean planting material and lowers the use of agrochemicals by reducing the spread of seed-borne diseases.
Implementing this model requires more than technical tools—it depends on strong government leadership, coordination, and commitment. Before adopting the approach, national authorities should clearly understand what is needed to create the right policy, institutional, and financial environment. The following points offer practical guidance to help governments prepare for effective implementation, starting with the first step: engaging with the lead technical partner.
Open source / open access
Scaling Readiness describes how complete a technology’s development is and its ability to be scaled. It produces a score that measures a technology’s readiness along two axes: the level of maturity of the idea itself, and the level to which the technology has been used so far.
Each axis goes from 0 to 9 where 9 is the “ready-to-scale” status. For each technology profile in the e-catalogs we have documented the scaling readiness status from evidence given by the technology providers. The e-catalogs only showcase technologies for which the scaling readiness score is at least 8 for maturity of the idea and 7 for the level of use.
The graph below represents visually the scaling readiness status for this technology, you can see the label of each level by hovering your mouse cursor on the number.
Read more about scaling readiness ›
Uncontrolled environment: validated
Common use by intended users, in the real world
| Maturity of the idea | Level of use | |||||||||
| 9 | ||||||||||
| 8 | ||||||||||
| 7 | ||||||||||
| 6 | ||||||||||
| 5 | ||||||||||
| 4 | ||||||||||
| 3 | ||||||||||
| 2 | ||||||||||
| 1 | ||||||||||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | ||
| Country | Testing ongoing | Tested | Adopted |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nigeria | –No ongoing testing | Tested | Adopted |
| Rwanda | Testing ongoing | –Not tested | –Not adopted |
| Tanzania | –No ongoing testing | Tested | Adopted |
This technology can be used in the colored agro-ecological zones. Any zones shown in white are not suitable for this technology.
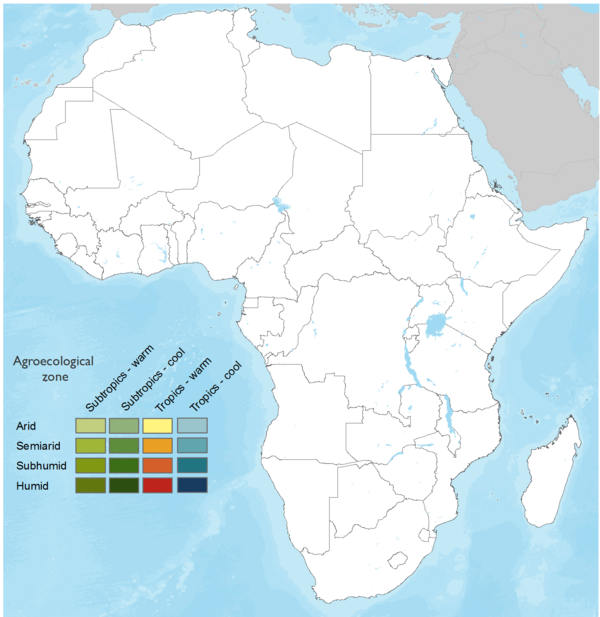




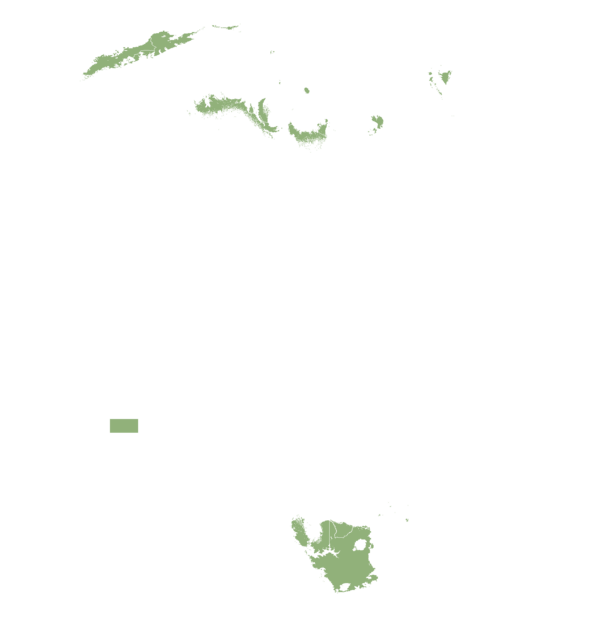
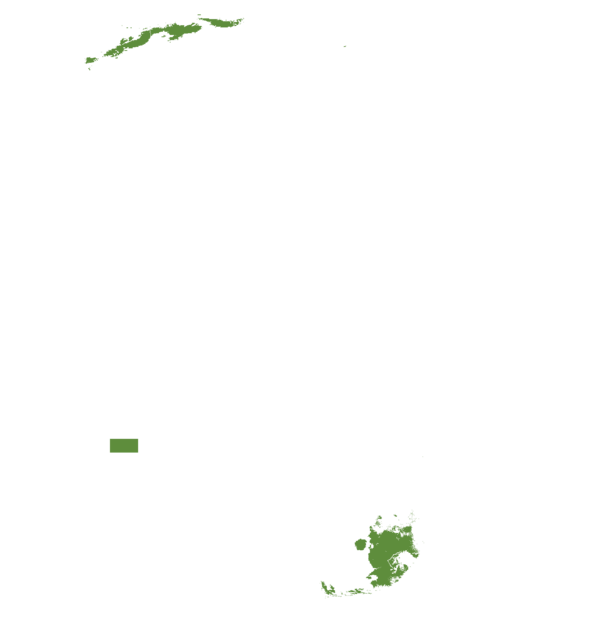







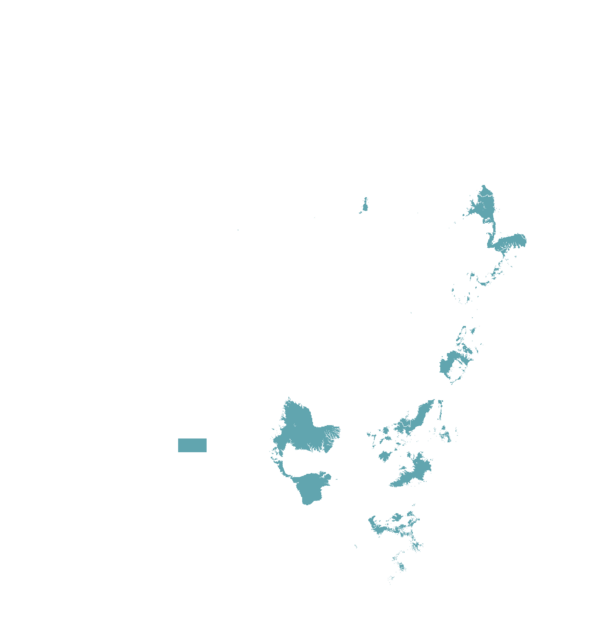


| AEZ | Subtropic - warm | Subtropic - cool | Tropic - warm | Tropic - cool |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Arid | ||||
| Semiarid | ||||
| Subhumid | ||||
| Humid |
Source: HarvestChoice/IFPRI 2009
The United Nations Sustainable Development Goals that are applicable to this technology.

Supports income generation for farmers and seed entrepreneurs by creating a sustainable, market-oriented seed system.

Improves food security through wider access to clean, high-yielding cassava varieties.

Promotes job creation and strengthens seed sector institutions, supporting rural economic activity.

Institutionalizes scalable innovations like digital seed certification and processor-led seed models.

Supports inclusive policies and local ownership, improving access for women and youth in rural areas.

Built on partnerships among governments, donors, research institutions, and the private sector for coordinated action.
Last updated on 28 November 2025